HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) formatting refers to the process of structuring and presenting content on a web page using various HTML tags. HTML provides a set of predefined tags that allow you to define the structure, layout, and visual appearance of your web page.
Here are some commonly used HTML formatting tags:
Bold Text
In HTML, you can apply bold formatting to text using the <strong> tag or the <b> tag. Both tags are used to indicate that the enclosed text should be displayed in a bold font weight. However, the <strong> tag has semantic meaning, indicating strong importance or emphasis, while the <b> tag is used purely for visual formatting.
Here's how you can use these tags to create bold text:
Using <strong> tag:
 |
| Strong Tag Code |
 |
| Strong Tag Preview |
Using <b> tag:
 |
| Bold Tag |
 |
| Bold Tag Preview |
Both of these tags will render the enclosed text with a bold font weight.
Italics Text
In HTML, italic text is represented using the <i> tag. The <i> tag stands for "italics" and is used to indicate a portion of text that should be displayed in italics. Italicizing text with the <i> tag also implies that the emphasized text carries some importance or emphasis within the context of the content.
Here's an example of how to use the <i> tag to create italicized text in HTML:
In the example above, the phrase "sample italic text" will be displayed in italics when rendered in a web browser.
Underline Text
In HTML, you can underline text using the <u> tag. The <u> tag is used to define and apply an underline style to the enclosed text. When the browser renders the HTML, the text within the <u> tags will be displayed with a line underneath it.
Here's an example of how to use the <u> tag to underline text:
Strike Text
In HTML, the strike-through effect is achieved using the <s> or <strike> tags. These tags are used to indicate that the enclosed text should be displayed with a horizontal line through it, typically to indicate that the text has been deleted or is no longer valid.
Here's an example of how to use the <s> tag:
 |
| Strike Tag Preview |
In the above example, the text "strikethrough text" will be displayed with a horizontal line through it, indicating that it has been struck out.
Monospaced Font
In HTML, a monospaced font is a typeface in which each character occupies the same amount of horizontal space. This means that every character, regardless of its width, is given equal space, resulting in a uniform appearance. Monospaced fonts are commonly used in programming, code snippets, and displaying text in a tabular format where alignment and spacing are crucial.
Here's an example:
 |
| Monospaced Tag |
 |
| Monospaced Tag Preview |
The monospace keyword is a generic font family that represents any monospaced font available on the user's system. The specific font families 'Courier New' and Courier are included as fallback options in case the user's system doesn't have the preferred font available.
Superscript Text
In HTML, superscript text refers to text that is displayed in a smaller size and raised above the baseline, typically used for footnotes, mathematical equations, or other instances where text needs to be displayed in a smaller, elevated format. To create superscript text in HTML, you can use the <sup> tag.
Here's an example of how to use the <sup> tag to create superscript text:
 |
| Superscript Tag |
 |
| Superscript Tag Preview |
You can apply the <sup> tag to individual characters, numbers, or even longer sections of text. It is often used in conjunction with mathematical or scientific notation, trademarks, or abbreviations.
Subscript Text
In HTML, subscript font is a formatting feature used to display text or characters in a smaller size and positioned slightly below the baseline of the surrounding text. It is typically used for scientific notations, chemical formulas, mathematical expressions, footnotes, or any other content that requires a lower positioning of characters.
To apply subscript formatting to text in HTML, you can use the <sub> tag. The text enclosed within the <sub> tags will be rendered as subscript. Here's an example:
 |
| Subscript Tag |
 |
| Subscript Tag Preview |
The resulting text will be displayed in a smaller size and positioned slightly below the baseline compared to the surrounding text.
Inserted Text
In HTML, inserted text refers to content that is specifically marked or annotated as an addition or insertion within the existing text. The <ins> tag is used to indicate inserted text in HTML.
Here is an example of using the <ins> tag to indicate inserted text:
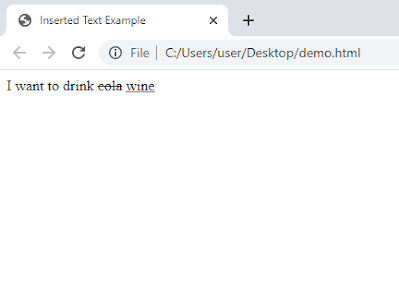
In the example above, the word "cola" is marked as deleted text using the <del> tag, and the word "wine" is marked as inserted text using the <ins> tag. This combination visually represents the change made to the original text.
Overall, the <ins> tag provides a way to indicate inserted or added text within an HTML document, helping to communicate changes and modifications made to the content.
Delete text
In HTML, there is no specific tag to delete or remove text directly. However, you can achieve the effect of deleting text by using the <del> tag. The <del> tag is used to indicate that a section of text has been deleted or removed from the content. It is typically displayed with a strikethrough line.
Here's an example of how to use the <del> tag:
 |
| Delete Tag |
 |
| deleted Tag Preview |
In the above example, the word "cola" will be rendered with a strikethrough line, indicating that it has been removed or deleted.
It's worth noting that the <del> tag is primarily used to represent changes made to a document or to show content that is no longer valid or accurate. It does not physically remove the text from the page but provides a visual indication that the text has been deleted.
Larger Text
In HTML, larger text refers to content that is specifically large or big size as an large or big within the larger text. The <big> tag is used to indicate larger text in HTML.
Here's an example of how to use the <big> tag:
 |
| Larger Tag |
 |
| Large Tag Preview |
In the above example, the text "larger text" will be displayed with a large size of word through it, indicating that it has been big.
Smaller Text
In HTML, smaller text refers to content that is specifically small or less size as an small or less within the smaller text. The <small> tag is used to indicate smaller text in HTML.
Here's an example of how to use the <small> tag:
 |
| Smaller Tag |
 |
| Small Tag Preview |
In the above example, the text "smaller text" will be displayed with a smaller size of word through it, indicating that it has been small.
Grouping
In HTML, grouping refers to the process of combining multiple HTML elements together as a logical unit or container. Grouping elements allows you to manipulate and style them collectively, apply common attributes, and structure the content more efficiently.
HTML provides several tags for grouping elements:









Comments
Post a Comment