Introduction
In MySQL, a data type is an attribute of a column that defines
what type of data the column can store. Understanding data types is
essential when creating tables and defining the structure of your
database. In this guide, I will explain the different data types in
MySQL and when to use them.
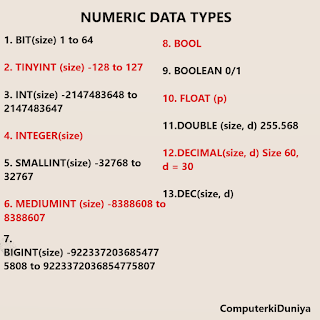
Numeric Data Types
Numeric data types are used for storing numeric values,
such as integers and decimals. The following numeric data types are
available in MySQL:
INT
The `INT` data type is used for storing integer values. It can
store values from -2147483648 to 2147483647. The size of an
`INT` column can be specified as a length, such as `INT(11)`. The
length is optional, but it is used for display purposes only and does not
affect the range of values that can be stored.
BIGINT
The `BIGINT` data type is used for storing large integer values. It can
store values from -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807. The size of a
`BIGINT`
column can be specified as a length, such as `BIGINT(20)`.
DECIMAL
The `DECIMAL` data type is used for storing decimal values with a
fixed precision and scale. The precision is the total number of digits, and
the scale is the number of digits to the right of the decimal point. For
example, `DECIMAL(10,2)` can store values with up to 10 digits, and 2
digits to the right of the decimal point.
Character Data Types
Character data types are used for storing string values, such as names,
addresses, and descriptions. The following character data types are available
in MySQL:
VARCHAR
The `VARCHAR` data type is used for storing variable-length string
values. It can store up to 65,535 characters, but the actual length is
determined by the length of the data being stored. For example,
`VARCHAR(255)` can store up to 255 characters.
CHAR
The `CHAR` data type is used for storing fixed-length string values.
It can store up to 255 characters, but the length is fixed and padded with
spaces if the actual data is shorter than the specified length. For example,
`CHAR(10)` will always store 10 characters, even if the actual data
is shorter.
TEXT
The `TEXT` data type is used for storing large string values, such as
documents, emails, and web pages. It can store up to 65,535 characters.
Date and Time Data Types
Date and time data types are used for storing date and time values,
such as birthdays, appointments, and events. The following date and time
data types are available in MySQL:
DATE
The `DATE` data type is used for storing date values in the format
'YYYY-MM-DD'. It can store dates from '1000-01-01' to '9999-12-31'.
TIME
The `TIME` data type is used for storing time values in the format
'HH:MM:SS'. It can store times from '-838:59:59' to '838:59:59'.
DATETIME
The `DATETIME` data type is used for storing date and time values in
the format 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'. It can store dates and times from
'1000-01-01 00:00:00' to '9999-12-31 23:59:59'.
TIMESTAMP
The `TIMESTAMP` data type is used for storing date and time values in
the format 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'. It can store dates and times from
'1970-01-01.



Comments
Post a Comment